Top 10 Site Structure Ranking Factors, Part 1 of 2
Contents
Often when you hear Matt Cutts talking about what makes for a good site, you’ll hear him mention that it has a good site structure and is easily crawlable. The main example he gives is that an important page shouldn’t be buried 15 pages deep. I feel that advice isn’t very actionable, because most websites, (especially those built on WordPress and less than 100 pages), would never be much deeper than 3 clicks from homepage.
I put together a list of what I feel are the top 10 ranking factors when it comes to site structure. I’m going to skip the condescendingly obvious suggestions such as “make sure your pages link to your homepage”. Yes, of course that’s nice, but if you’re using WordPress that’s already taken care of. Following then are suggestions about site structure issues which may not be that obvious.
Links in Content
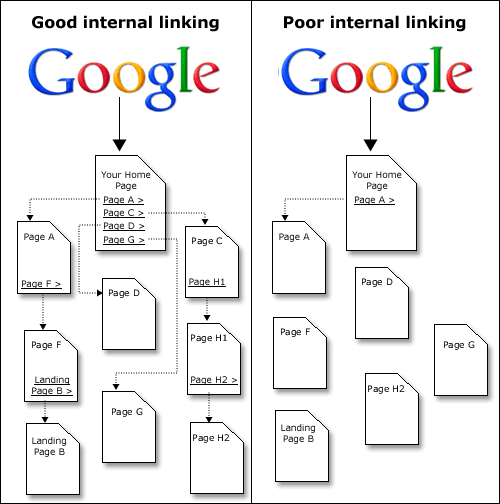 When you think of site structure, it’s all about how the pages of your site interact with each other. The most powerful type of inter-site linking happens when you link in content to other relevant pages to your site, where the context of the outgoing link in your article is relevant to the page with the inbound link.
When you think of site structure, it’s all about how the pages of your site interact with each other. The most powerful type of inter-site linking happens when you link in content to other relevant pages to your site, where the context of the outgoing link in your article is relevant to the page with the inbound link.
Many people are guilty of building sites that do not link to other pages of the site, in content. They rely on plugins to generate related links inside the template, or they simply leave internal linking to the navigational menu. This, quite frankly, is leaving money on the table. It’s so easy to build relevant links between your various pages, and this has the strongest impact on your rankings than any other site structure change you could do.
Every article on your site is an opportunity to prop up other pages on your site with these internal links. You should have at minimum, two or three links per article, where a page will do this inter-linking. By using this technique, your site can be ranking under the weight of its own internal links.
Relevancy of Internal Links
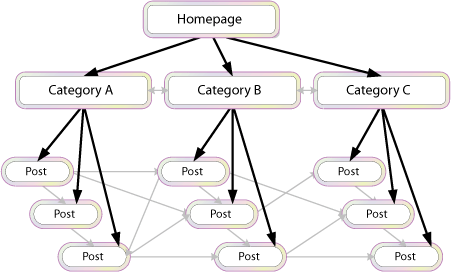 I briefly mentioned that the links should be relevant. Let me explain more about that here. Both your internal linking (inside of content), and your navigational links, should as a best practice link only to other relevant content on your site.
I briefly mentioned that the links should be relevant. Let me explain more about that here. Both your internal linking (inside of content), and your navigational links, should as a best practice link only to other relevant content on your site.
There is a popular linking method called “siloing”. If you’ve heard that buzzword, a simple explanation of it would be that the navigation system links to root categories, and only the root categories are shown throughout the site on every page. However, as you explore a root category, you see other subcategories, and those subcategories could have their own. The idea is that unrelated subcategories do not link to every other subcategory on the site, but the links are reserved for only the most relevant pages in the same subcategories. My reason for mentioning siloing is that the thing that makes it work is the relevancy of the internal linking.
By far the easiest way to promote relevant internal linking is to use a plugin, such as YARPP (yet another related posts plugin). This plugin selects other pages on the site that are most relevant, based on title, category and the content of the body. By algorithm, the top most related pages are linked to. This is the second most powerful way to interlink within your website, aside from links in-content.
Site-Wide Relevancy of Content
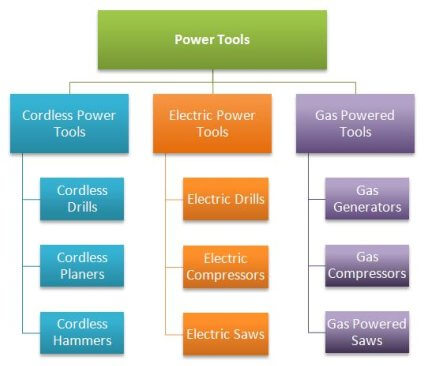 It would only follow that if links within relevant content is powerful, that your articles should somehow be related. If you are building a money site that is based around a niche, it’s a good idea that your articles all stay relevant to that niche. This ties in with Author Rank, where Google endeavors to discover authors of content that are relevant to a particular niche.
It would only follow that if links within relevant content is powerful, that your articles should somehow be related. If you are building a money site that is based around a niche, it’s a good idea that your articles all stay relevant to that niche. This ties in with Author Rank, where Google endeavors to discover authors of content that are relevant to a particular niche.
If you’re building and promoting your site properly, you will establish social accounts for your website. These social accounts will begin accumulating “author rank”, as it pertains to the particular niche that you write about. Therefore, it is a good idea if your articles are all related to each other. It would make sense to create a website that has a health focus, where it may have sub categories of yoga, jogging, exercise, eating healthy, etc. These topics are close enough, that your author rank would accrue a general health niche relevancy. However, if you also wrote about other completely unrelated topics, such as real estate, that would dilute your overall relevancy.
As this is an article on site structure ranking factors, it would be great for the structure of your site if your pages are all related. By focusing on one niche, you show Google that you are an expert in that topic. It also makes sense as the relevancy of your pages will be boosted as each internal page is related to the others.
One way to look at this is, if you’re a dog training website, would you want links from pet supply stores and a pedigree dog association? Or would you rather get links from a marketing site? Obviously, when it comes to external links, you want links from relevant sources. This is also true for your own internal content. The best site structure is built around relevant content.
Diversity of Content
 If your content is diverse, it will rank well and be an asset on your site. If it is an article that says essentially the exact same thing as other sites on the internet (even though exact wording changes), Google will filter these types of results from their results. Google has a sophisticated algorithm to weed out articles that are essentially saying the same thing. This applies to low quality spun content (articles that have various synonyms swapped to make the article read differently, yet essentially say the same thing), and it also applies to where someone rewrites someone else’s article, without adding new points or diversifying it’s content.
If your content is diverse, it will rank well and be an asset on your site. If it is an article that says essentially the exact same thing as other sites on the internet (even though exact wording changes), Google will filter these types of results from their results. Google has a sophisticated algorithm to weed out articles that are essentially saying the same thing. This applies to low quality spun content (articles that have various synonyms swapped to make the article read differently, yet essentially say the same thing), and it also applies to where someone rewrites someone else’s article, without adding new points or diversifying it’s content.
Google has filed a patent on diversity filtering. A quick definition of this diversity filtering is as follows:
To determine the link quality score, the link engine can perform diversity filtering on the resources. Diversity filtering is a process for discarding resources that provide essentially redundant information to the link quality engine.
The reason I bring this up in a site structure ranking signals article is to make this point: the foundation of your site is built on unique and diverse articles. If a significant portion of your site structure involves articles that are lower quality rewritten content, then those pages are not only filtered from the search engine result pages,the value they pass to the other pages on your site via internal linking is bound to be lower.
The way to combat this problem is to make certain the articles you’re having written for your site aren’t just rewritten articles from someone else’s site. Tell your article writers that you need content that is diverse. Explain that your articles need to approach a topic from different angles. This is true, not only of the content on your site, but of the blogs and other sources where you build links to your site.
Duplicate Content
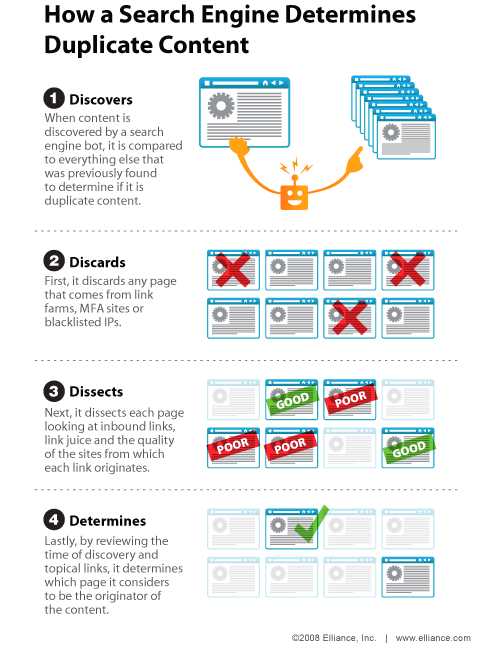 I think that everyone understands that duplicate content is only going to get your site in trouble. However, I wanted to make an example of when it is ok to use duplicate content. If you’ll notice, I often quote sources, as I link to them, and discussing the merits of things that other people have written. This results in a paragraph of their content ending up in the articles I’ve written. This, I believe, is a normal practice, and Google isn’t going to slap a penalty on your site if you have a moderate amount of duplicate content on your site from an activity such as this.
I think that everyone understands that duplicate content is only going to get your site in trouble. However, I wanted to make an example of when it is ok to use duplicate content. If you’ll notice, I often quote sources, as I link to them, and discussing the merits of things that other people have written. This results in a paragraph of their content ending up in the articles I’ve written. This, I believe, is a normal practice, and Google isn’t going to slap a penalty on your site if you have a moderate amount of duplicate content on your site from an activity such as this.
Then, there are other issues of when duplicate content arise, such as when WordPress takes the initial paragraph of your article and replicates it on your archives page, tag pages, category and homepage. This is a major flaw that WordPress inflicts upon your site structure. I’ll discuss the best ways of dealing with these types of duplicate content on the next page.
Finally, if your duplicate content comes from that which was scraped from other sites, it will not be beneficial to your rankings. You’ll suffer from the same issue as the “diverse content”, where your pages will be filtered from Google’s SERPs. This is a structural flaw, because these filtered pages become like a black hole on your site, where positive link juice is flowed in, but does not come out and continue flowing through your site, because the quality of the content is bad.
Thanks for reading the first half of our site structure ranking factors article. Continue through to the next page to read about site structure issues #6 through #10.

Comments